Entity Store In Processors
You can find the general entity definition in entities
Accessing Data in Processor
After defining the schema, you can use sentio build to generate the TypeScript types for the schema. The generated files is located in the src/schema directory. The following is an example of the generated types:
type UserData = Omit<User, "rewards"> & {rewards?: Array<ID|Reward>}
@entity("User")
export class User extends Entity {
constructor(data: Partial<UserData>) {
super(data)
}
get id(): ID { return this.get("id") }
set id(value: ID) { this.set("id", value) }
get name(): String { return this.get("name") }
set name(value: String) { this.set("name", value) }
}
The generated types can be used to access the data in the processor. use ctx.store to interact with the data store.
Insert or Update Data
To insert or update data in the store, you can use the ctx.store.upsert method. The following is an example of inserting a new user:
import { User } from './schema/schema.js'
ERC20Processor.onEventTransfer(
async (event, ctx) => {
const from = new User({
id: event.args.from
})
await ctx.store.upsert(from)
const to = new User({
id: event.args.to
})
await ctx.store.upsert(to)
}
)
Get entity by ID
To retrieve an entity by its ID, you can use the ctx.store.get method. The following is an example of retrieving a user by its ID:
import { User } from './schema/schema.js'
ERC20Processor.onEventTransfer(
async (event, ctx) => {
const from = await ctx.store.get(User, event.args.from)
const to = await ctx.store.get(User, event.args.to)
}
)
Delete entity
To delete an entity, you can use the ctx.store.delete method. The following is an example of deleting a user:
import { User } from './schema/schema.js'
const id = event.args.from
await ctx.store.delete(User, id)
Query entities
In your store, there are two methods to query and filter entities: list and listIterator.
store.list(Entity, filters)
store.list(Entity, filters)For simplicity, the list method returns entities based on the Entity and filters parameters.
The following is an example of querying all users with an amount greater than 0:
import { User } from './schema/schema.js'
ERC20Processor.onEventTransfer(
async (event, ctx) => {
// Get all users with amount greater than 0
const users = await ctx.store.list(User, [{field:"amount", op:">", value: 0}])
for (const user of users) {
console.log(user)
}
}
)
Please be aware that the list method retrieves all entities, which might not be optimal and could potentially consume a lot of memory resources in your processor. For handling larger datasets, we recommend using the listIterator method.
store.listIterator(Entity, filters)
store.listIterator(Entity, filters)The listIterator method returns an iterator that can be used to iterate over entities based on the Entity and filters parameters.
You can use the for await grammar to iterate over the entities.
ERC20Processor.onEventTransfer(
async (event, ctx) => {
for await (const user of ctx.store.listIterator(User, [{field:"name", op:"=", value: "Alice"}])) {
console.log(user)
}
}
)
Unlike the list method, the listIterator method does not load all entities into memory at once,
you can handle entities one by one, or in batches, which is more memory-efficient.
The following is an example of handling entities in batches:
ERC20Processor.onEventTransfer (
async (event, ctx) => {
const iterator = ctx.store.listIterator(User, [{field:"name", op:"=", value: "Alice"}])
let batch: User[] = []
let promises: Promise<any> = []
for await (const users of iterator) {
batch.push(users)
if (batch.length >= 10) {
promises.push(handleBatch([...batch]))
batch = []
}
// you can use `break` to stop the iteration
// if (promises.length > 100) break
}
// handle the last batch
if (batch.length > 0) {
promises.push(handleBatch([...batch]))
}
// wait for all promises to complete
await Promise.all(promises)
}
)
Filters
The filters parameter is an array of objects that specify the filter conditions. Each object has the following fields:
-
field: The field name to filter on. -
op: The operator to use for the filter. The supported operators are:=: Equal!=: Not equal>: Greater than>=: Greater than or equal<: Less than<=: Less than or equalin: In the listnot in: Not in the list
-
value: The value or the array of values to filter on.
Multiple filters are combined using the logical AND operator.
The following is an example of querying all users like the where amount > 0 AND name = 'Alice' in SQL:
ctx.store.listIterator(User, [
{field:"amount", op:">", value: 0},
{field:"name", op:"=", value: "Alice"}
])
Query Data using SQL
You can query the data store using SQL. Just like you do with event logs data. The entity will show up in table schema.
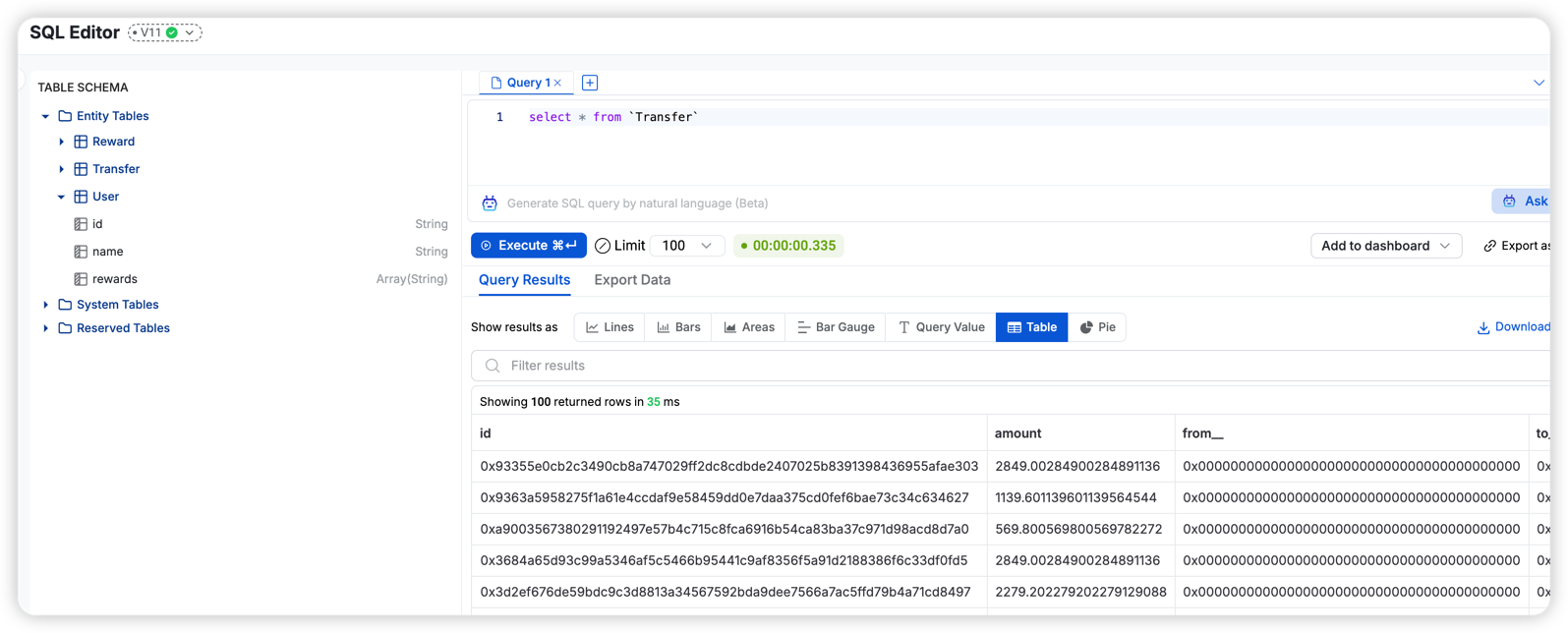
Query Data using GraphQL
You can query the data store using GraphQL. The query schema will be generated based on the schema definition.
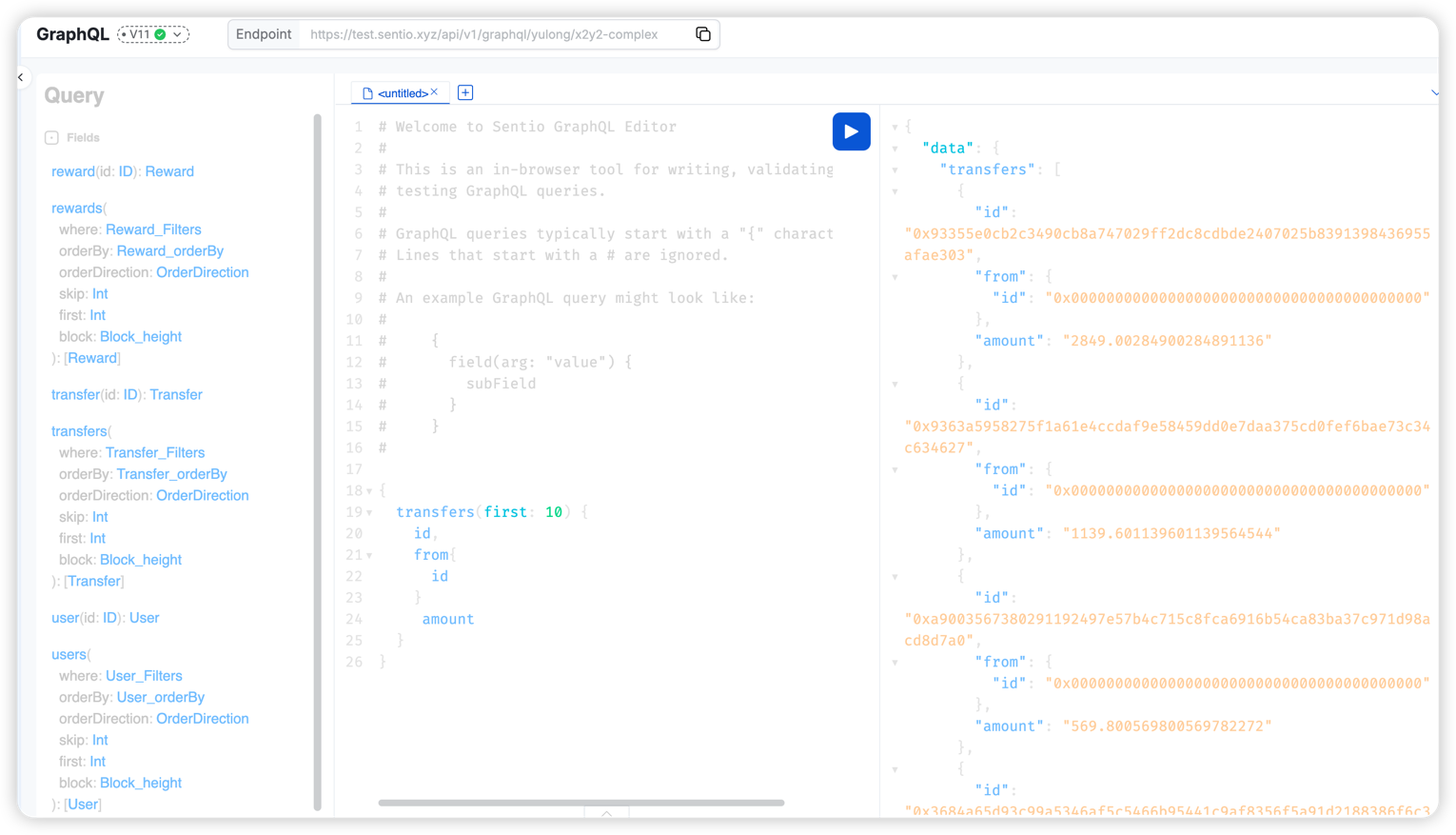
Updated 4 days ago
